Summary
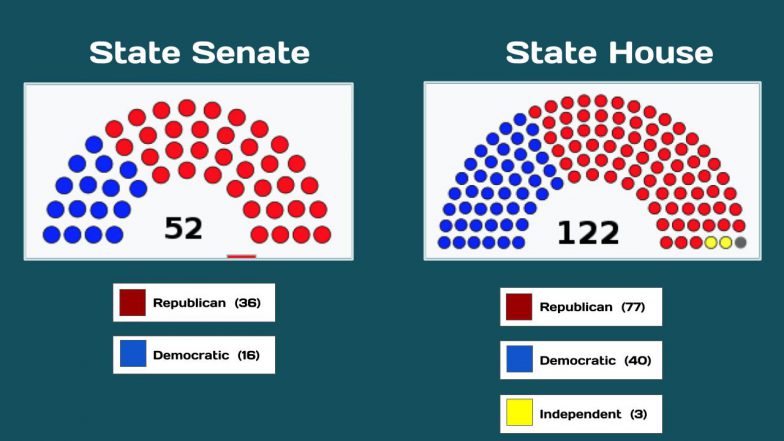
The Mississippi Legislature is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Mississippi. The bicameral Legislature is composed of the lower Mississippi House of Representatives, with 122 members, and the upper Mississippi State Senate, with 52 members. Both representatives and senators serve four-year terms without term limits. The Legislature convenes at the Mississippi State Capitol in Jackson.
OnAir Post: MS Legislature
News
Mississippi Today, – March 22, 2021
The legislative roads for two of the most high-profile issues of the 2021 session — a massive tax swap proposal and the legalization of medical marijuana — appear to have reached a dead end.
While the ability of Mississippi legislators to revive an issue should never be underestimated, it appears the joint rules would make it near impossible to bring back to life both issues.
The end came quietly when House Judiciary B Chair Nick Bain, R-Corinth, made a motion to go to conference on a Senate bill that contained the language legalizing medical marijuana. Senate Finance Chair Josh Harkins, R-Flowood, did the same for the House bill that would have enacted the tax swap. Both motions were approved with no fanfare.
About
Source: Wikipedia
History
The Mississippi Legislature was created as the Mississippi General Assembly in 1800, when Mississippi was still a territory.[2] Starting in 1833, it became known as the Mississippi Legislature.[2]
Powers and process

This brick church was erected in Washington, Mississippi in 1816. The first Constitution of Mississippi was written and adopted here; the state’s first legislature convened here in 1817. The preliminary treason trial of Vice President Aaron Burr occurred under some nearby oak trees.[3]
The Constitution of Mississippi gives the state legislature the authority to determine rules of its own proceedings, punish its members for disorderly behavior and expel a member with a two-thirds vote of the membership of his or her chamber.[4]
A bill may originate in either house, and be amended or rejected in the other, and must be read by its title on three different days in each house, unless two-thirds of the house dispenses with the rules.[4] The Mississippi Constitution prohibits amending a bill to change its original purpose.[4] Bills amended in the second house, must return for a vote to accept amendments.[4]
The Governor of Mississippi has the power to veto legislation, but legislators can override the veto with a two-thirds decision.
Membership
Members of the Mississippi House of Representatives are elected to four-year terms and Mississippi State Senators are also elected to four-year terms.
See also
- Mississippi State Capitol
- Mississippi House of Representatives
- Mississippi Senate
- Political party strength in Mississippi for party compositions
Note
- “2018 Legislator Compensation Information”. NCSL.org. National Conference of State Legislators. Retrieved May 14, 2019.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Rowland, Dunbar (1908). The Official and Statistical Register of the State of Mississippi. Department of Archives and History. p. 272
- “Mississippi Pictorial History, 1798-1937”. Mississippi Historical Research – W.P.A. Project. 1937.
- ^ Constitutional Provisions The Legislature And Legislation Rules of Procedure, Mississippi Legislature (accessed May 27, 2013)